Zero Trust Security
Understand the fundamentals, key principles, standards, and best current practices.
Zero Trust Security Standards
What is Zero Trust?
The foundation of Zero Trust Security is switching from a perimeter-based (firewall and VPN) model of access to a user-to-resource model.
It means implementing strong, simple identity for both people and also a system. Decouple the identity from the corporation to make it affinitive to the user—a single identity.
Through it, you can enforce entitlements and authorization in the network.
This micro-segmentation is simpler to use, more accessible, and, more secure. It reduces the lateral traversal, empowers your users, increases your audit capabilities, is more economical, and is more scalable. This is the power of Zero Trust.
Identity
The core of any Zero Trust Architecture is identity. Identity of a person, identity of a resource. Users are commonly identified via OpenID Connect and SAML. Resources are commonly identified by Client Certificates.
The Global Identity Foundation. A single global identity for all humanity.
OpenID Connect. A simple identity layer on top of OAuth 2.0
OAUTH2. The industry standard protocol for authorization. RFC 6749.
Security Assertion Markup Language (SAML). An XML-based framework for communicating user authentication, entitlement, and attribute information.
W3C Web Authentication (WebAuthN). Strong, attested, scoped public key-based credentials for web applications for authenticating users.
Zero Trust Architecture
Zero Trust Architecture has evolved over the years. The constant theme is changing from a perimeter-based (firewall+VPN) security stance to a user+resource stance.
NIST SP 800-207 Zero Trust Architecture. Evolving cybersecurity defense from static network-based perimeters to focus on users, assets, and resources.
Zero Trust Security Architecture: The Open Group.
Jericho Forum. An early users group facilitated by the Open Group who pioneered De-Perimeterization.
Foundational
Zero Trust Security has a set of foundational standards that are shared with other technologies. These relate to cryptography, security, and identity.
JSON Web Token (JWT) (RFC 7519)
The Transport Layer Security (TLS) Protocol Version 1.3
Secure Production Identity Framework for Everyone (SPIFFE)
Best Practices
JSON Web Token Best Current Practices (RFC 8725)
OAuth 2.0 Security Best Current Practice
OpenID Security Best Practices
-
CityNews The Mike Farwell Show Interview
This morning I was interviewed on the Mike Farwell Show (CityNews). You can check the interview here @ 54:50.
-

SolarWinds Gives Federal Agencies Labour Day Present
SolarWinds Web Help Desk CVE-2024-28986 (rated 9.8 our of 10) is now included in CISA’s Known Exploited Vulnerabilities (KEV) Catalog, indicating its active use in cyber attacks, giving affected agencies until September 5, 2024 to fix the flaw under Binding Operational Directive 22-01. How fun.
-
10 Billion Reasons Shared Passwords Are Bad: RockYou2024
Shared password bad. 10 billion passwords leaked. Your team installed some shadow IT remote access solution with a shared password.
-
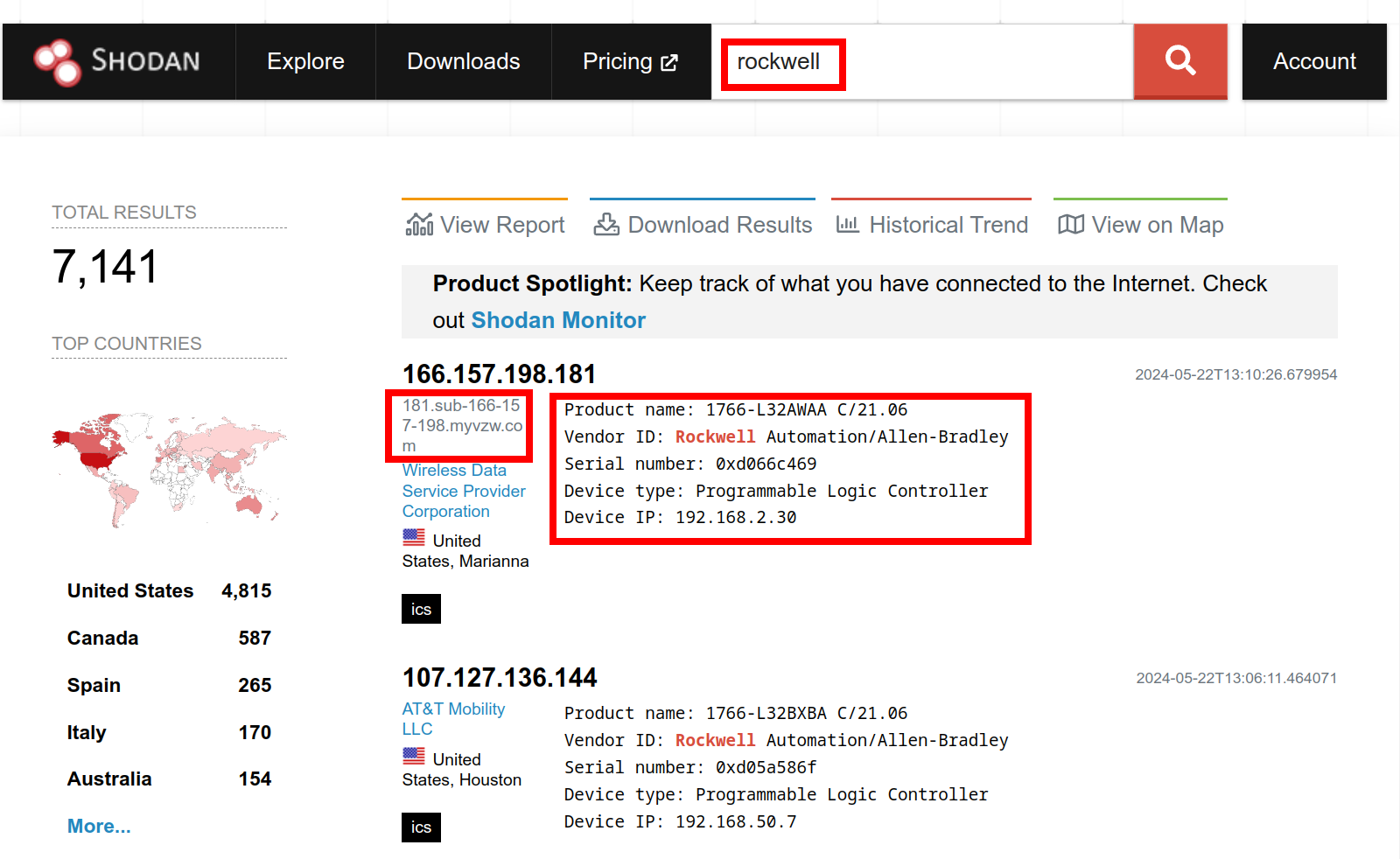
Get Thee From BGP Rockwell: Ethernet/IP Is not Internet
You wouldn’t download a PLC, would you? Rockwell Automation alert on public access to PLC, and a Shodan search to fact check it.
-

Begone Ivanti Industrial VPN Sayeth CISA
ED 24-01 directs agencies to instantly remove Ivanti Industrial VPN from industrial operations. Defence In Depth, Zero Trust give you more time to react.
-

Using Zero Trust to Enable Secure Remote Access to SCADA for Water Systems
This blog post explores the challenges of securing remote access to SCADA systems and how Zero Trust can act as a solution.
-

Zero Trust vs. VPN: A Comprehensive Comparison for Secure Remote Access
In this blog post, we’ll dive into the Zero Trust vs. VPN security model differences and why the former is ultimately the far superior choice for secure, seamless remote access.
-

SSH for Remote Access: Every User, Every Device, Every Application
In this blog post, we’ll delve into the challenges of enabling SSH for remote access and how you can do so without compromising security through Zero Trust.
-
Simplifying Secure Access: Enabling Rockwell Automation Remote PLC Access Without a VPN
In this post, we’ll explore the limitations of VPNs and delve into how to enable Rockwell Automation remote PLC access.
-
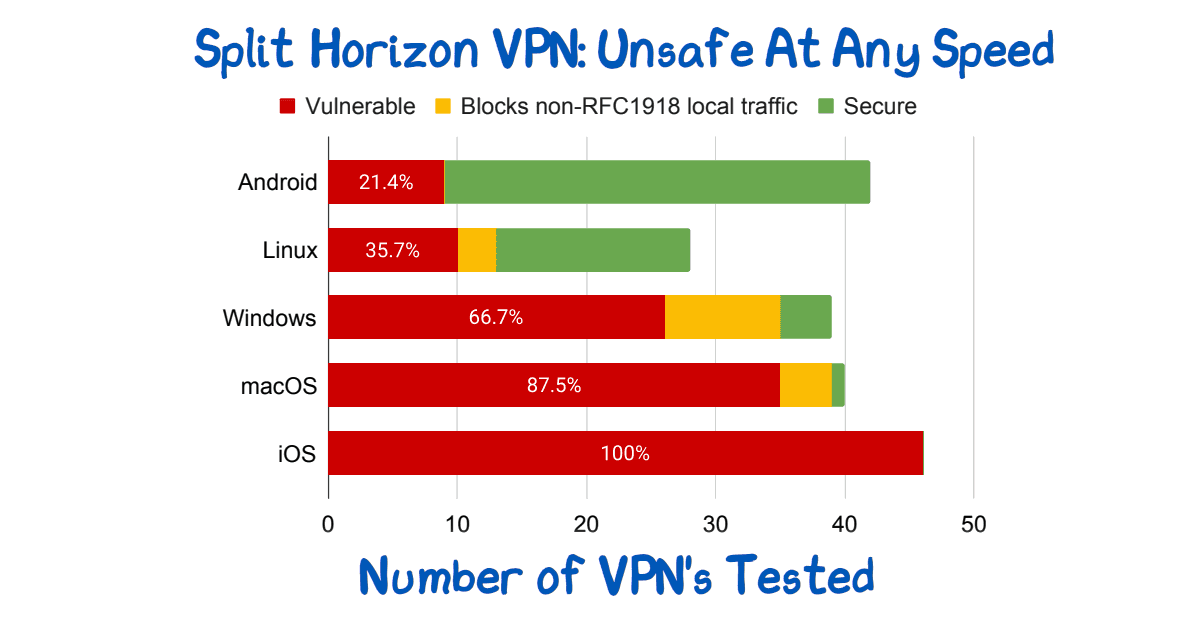
Split Horizon VPN: Unsafe At Any Speed
Split Horizon VPN’s are used to avoid breaking video conferencing. They are unsafe. See paper for route injection issues.
-

NIST sp 800-63A: Introduce Yourself
Who are you? Identity involves knowing who you are, and then later proving it. NIST sp 800-63A enrollment is the first step, let’s talk about that!
-

The Security Risks of Using VPNs in Water and Wastewater Facilities
What are the risks of using VPNs in water and wastewater facilities? We’ll help you answer that question and understand what to do instead.
-

The Security Risks of Using Shared Credentials in Water and Wastewater Facilities
There are many security risks of using shared credentials in water and wastewater facilities. Here’s why you should eliminate them and how to do it.
-
Zero Trust Troika: The Who, The What, The How
Perimeter security approaches are no longer effective. A Zero Trust Network Architecture is a powerful, modern way to protect your network from cyber attacks.
-

Strengthen Your Industrial Network Cybersecurity with Vendor Access Management
Securing your third-party vendors can help reduce the cyber risk to your control systems and improve overall industrial network cybersecurity.
-

Understanding the CISA Zero Trust Maturity Model: A Framework to Improve Your Security Posture
This article will give you an overview of the CISA Zero Trust Maturity Model, the changes made in Version 2.0, and how it can benefit your organization.
-

The Zero Trust Roadmap: Understanding NIST 800-207 and How to Align With It
This article will give you an overview of NIST 800-207 and the different ways your organization can implement Zero Trust to meet the guidelines.
-
Best Practices In Vendor Privileged Access Management
Vendor privileged access management best practices: Access control, strong, unified authentication, fine-audit, secure access.
-

Identity Provider Versus Single-Sign-On
Single-Sign-On and Identity Providers are often treated as the same. But, the IdP facilitates the SSO. You can have multiple IdP if desired.
-

Who Are You? Prove It! Identity Versus Authentication
Identity vs Authentication. Who are you. Prove it. Related but different concepts. Ensure your IdP does not give identity when it realy means authentication.
-
Another Day, Another Exploit – Protecting Against the ProxyNotShell Exchange Server Zero-Day Vulnerability
Learn how zero trust protects against the new Microsoft Exchange Server zero-day exploit affecting Outlook Web Access (OWA), ProxyNotShell. With Agilicus, you’ll block lateral traversal and prevent unauthorised traffic from arriving at your resources while ensuring they are still accessible to legitimate users.
-

Well Timed or Coincidental, Cue the Phishing Attacks as 2.5M Students Affected by Data Breach
Days after announcing student loan forgiveness in the United States, 2.5 million student borrowers had their personal information exposed in a data breach and are at an increased risk of being targeted in a phishing attack.
-

Protecting Against the OWASP Top 10 Web Application Vulnerabilities
The OWASP Top 10 is a standard awareness document that outlines the most critical web application security risks and vulnerabilities. Learn how Agilicus AnyX is designed to eliminate an attacker’s visibility into the potential OWASP Top 10 web application vulnerabilities.
-

Industrial Air Gap – A Tale Of 2 Users
Industrial devices are hard to secure. Commonly done only via direct local access. Teams, however, wish remote access to improve efficiency. A solution to this battle is Zero Trust.
-

Top 5 Cybersecurity Resolutions to Cross off Your List in 2022
Cybercriminals had a record year, the cost of a breach reached new highs in 2021. With clear cybersecurity goals, businesses avoid becoming a news headline.
-

NIST sp 800-63A: Introduce Yourself
Who are you? Identity involves knowing who you are, and then later proving it. NIST sp 800-63A enrollment is the first step, let’s talk about that!
-
NIST sp 800-63B: How Well Do I Know You?
Zero-Trust Network Architecture has 3 steps: Authenticate (Who), Authorise(What), Access(How). 3 Levels of strength of the who are defined in NIST sp 800-63B. Does the goldilocks principle apply to you? Read on!
-
Zero-Trust Remote Access to Fix VoIP DDoS
Reconfigure a VoIP PSTN gateway remotely via Zero Trust with Multi-Factor Authentication and single-sign-on to avoid a DDoS.
-

Authentication, Authorisation, and API Keys
e encouraged to create API keys by many SaaS tools, and, these present real authorisation challenges.
-
Mind the gap between the web app and the desktop
We want a web app. We have a desktop. Use zero-trust to make any desktop available to any device without a VPN.
-

A ’round tuit’ to get your internal web apps available
You have an internal tool. Grafana, Prometheus, …. You get an alert, its via Slack, Chat, etc. You click. The link goes nowhere. You curse. We fix!
-
The Pipeline Ransomware Came Via The VPN
A criminal group takes over a nations energy via a VPN. Its time to treat the VPN as a risk, not a security solution. Zero Trust is better.
-
SSH To Server. No IP? No Problem!
SSH to the server fleet. No Public IP? No problem. No VPN. No firewall changes. End-to-end encryption. Any user.
-

Keep The Share, Ditch The Ransomware With Zero Trust
Keep The Share. Ditch The Ransomware. Simple Zero-Trust allows any user, any device, any share, no VPN, no ransomware. Simple single sign-on.
-

Zero Day Zero Trust Is Your Defense in Depth
Zero Trust. The principle of limiting access to user resource pairs. It is part of a good defense in depth strategy. It is also a key defense to Zero Day.
-

SCADA, Zero-Trust, Content-Security-Policy
A Florida water treatment plant breached. People nearly poisoned. SCADA exposed via Windows & TeamViewer. How did it happen, how do we prevent systematically?
-

Quis, quid, cur, quomodo, ubi, quando, quibus auxiliis
Grade 10 English, the W5 (Who, What, Why, When, Where, How). A common framework to frame something. Apply it to the problem domain of Zero Trust Networking.
-
Identity Sprawl And Shadow IT
Empowered people make pragmatic decisions to improve productivity. This can create Shadow IT, and, Identity sprawl. Fix via Identity Aware WAF
-

Better Than Nothing Bonding With Remote Access: Starlink + 2xDSL Backup
Deploy OpenWRT on a Mikrotik to achieve SpaceX Starlink + bonded DSL backup, with Zero-Trust Network Access inbound from any user, any network, any device.
-
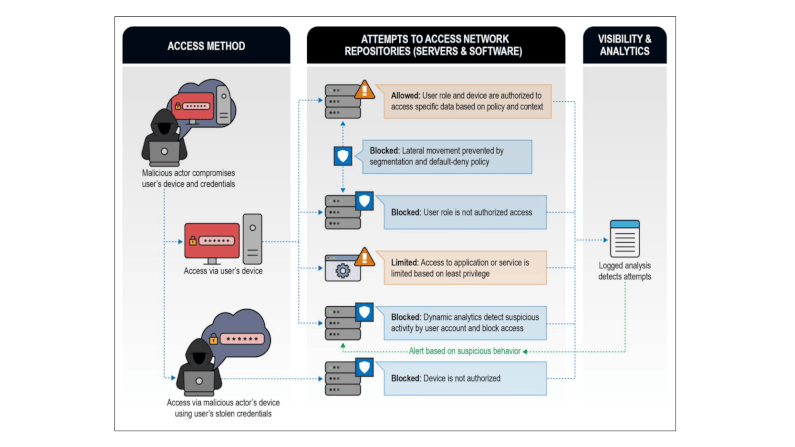
Embracing Zero Trust Security Model: NSA Guidance
Embracing Zero Trust: Assume that a breach has (or will occur), use defense in depth, fine grained authorisation and audit, everywhere, always.
-

Remote QuickBooks Share Access Without The VPN
Access your QuickBooks from anywhere, as any user, without a VPN. Live. No export. No ransomware.
-

Time and Encryption are Inter-related: Certificate Transparency
Time and Encryption. Certificates have a not-before and not-after. If your time is wrong, you can be tricked. Learn how the certificate transparency helps you.
-
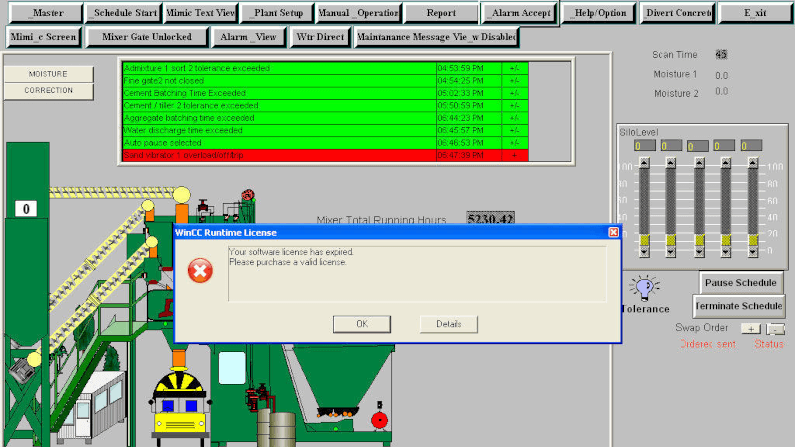
Zero Trust Secure SCADA Could Make Your Water Safe To Drink
A water treatment plant was breached, looking to poison people. How did the hacker get in, and how would zero-trust secure scada?
-

OAuth 2.0 Security Best Current Practice
OAuth 2.0 is deceptively simple: create client id, client secret, set a few environment variables, and watch the black magic take effect. Learn about the best current security practices.
-
OAuth 2.0 Protected Resource Threats
The OAuth 2.0 protected resource. It takes the access token and uses it to grant access. Watch out for it becoming compromised.
-

OAuth 2.0 Refresh Token Threats
OAuth 2.0 refresh tokens are used to obtain new access tokens on the user’s behalf. If lost, they can allow an attacker to masquerade.
-

OAuth 2.0 Token Endpoint Threats
The OAuth 2.0 Token Endpoint. Its were authorisation becomes real. Secure it to prevent guessing
-

Your password policy is wrong: NIST SP 800-63B
Your password policy is wrong. So says this NIST standard. By trying to be too strong, you end up being weak. The users write it down!
-

OAuth 2.0 Authorisation Endpoint Threats
OAuth 2.0 Authorisation Endpoints are the front-door skeleton-key creator of all your front-doors. So protect them carefully.
-

OAuth 2.0 Client Threats
OAuth 2.0 and the client. Use Defense In Depth. Secure the client, and then assume it can still be compromised. Zero Trust.
-

OAuth 2.0 Threat Model and Security Considerations
OAuth 2.0 has simplified authentication and authorisation for many applications, shifting from custom code to simple library import. However, as more applications come to rely on it, this makes its weaknesses more interesting. An attacker can gain access to a broader set of data via a smaller set of tactics and techniques. First lets understand the threat areas, and then, the best current practices for addressing them.
-
Merger, Acquisition: Federated Identity And Zero Trust
Merger Acquisition Zero Trust. Two competitive or orthogonal companies become one. Achieve quick and secure with Federated Identity, Zero Trust.
-

Joint Venture: The Case For Federated Identity And Zero Trust
Joint Ventures: Good Business strategy, complex access strategy. Does one VPN to the other? Dual accounts? Zero Trust Federated Identity FTW!
-

Zero-Trust Reduces Ransomware Risk
Target ransomware with Zero Trust. Defense in Depth with better audit, reduced access, increased simplicity.
-
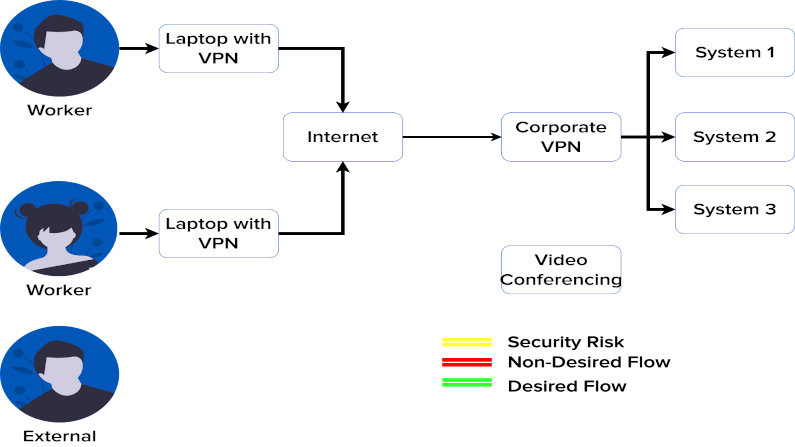
Your VPN Hates Your Video Conferencing. Here’s Why
Got VPN? Got perfect video conferencing with everyone all the time? If yes, well, this video is not for you. For the rest, read and view!
-

Zero Trust Audit Logging: Reliable Meets Simple
Big investments in SIEM become big headaches due to correlating IP and NAT. Skip that with crypto-secure audit with Zero Trust via JWT.
-

Reject The Status Quo: Zero Trust Status Future
The myth of the VPN, the Firewall as the only and best method of remote access has lived for 20 years. Let’s retire it together. I discuss the myth, and, an outbound-only, no firewall reconfiguration method, no client method of achieving your goals of happier productive users accessing their data and applications.
-
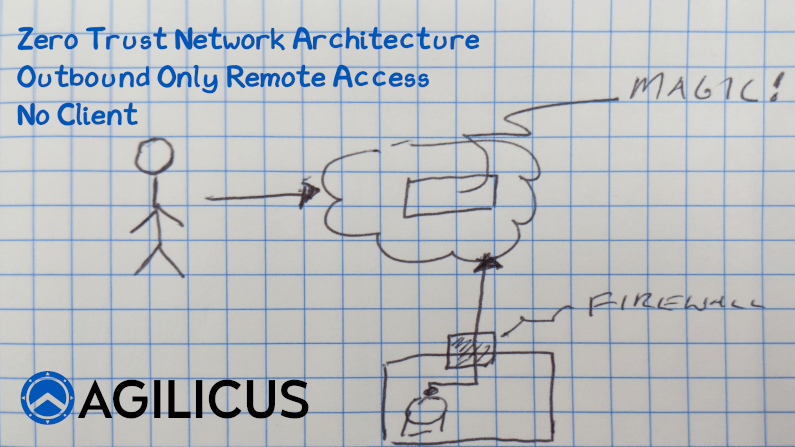
Access an Internal Resource with no Inbound Connections
Learn how to implement Zero Trust Network Access with no inbound connections, no firewall changes.
-

You want me to sign in with what now?
“Sign in with…”. What does it mean? Why should I use it? What am I giving up? There must be a catch, right?
-

Identity, Authorisation, Access: Microsoft Dynamics
Single Sign On with Microsoft Dynamics. First decide what this means, to who it means what. Then find a way to federate their natural, native identity providers together.
-

Ding Dong: The VPN is dead. Split Identity and Authorisation to Simplify Security
A philosophy that allows you to reduce cost, increase security, and increase user engagement and satisfaction. All 3 at once. Sounds crazy?
-
Trust You? I Just Met You! How Trust-On-First-Use Can Increase Your Security
Trust-On-First-Use for enrolling multi-factor authentication.can improve your security for lower cost. Sounds like a win to me!
-
The False Choice of Risk Versus Reach
Risk versus Reach. A false choice. We should not materially compromise security to reach more users.
-

Why your VPN is slow: the case of the work-at-home streaming
VPN slow? It might be your friends using YouTube and Spotify. Ration bandwidth? Split Horizon? We recommend door #3: Zero Trust, Internet Exposed, Direct.
-

Zero-Trust Makes Working From Home Secure And Reliable, Unlike VPN
A sudden influx of remote workers is stressing the VPN. That stateful device struggles. Consider a future switch to Zero-Trust, secure remote access with it.
-

Zero-Trust Principles
The principles of zero trust make for improved security. Each component must prove itself to its neighbours. No trust is based on affinity or path. Explore.
-

Secure Exposed Access: Zero-Trust Legacy Online With High Security and No Work
Somewhere in your basement lurks a challenge. A web application that people need, but you don’t trust. Maybe its your timesheet or vacation planner. Maybe its your HR policies portal. But you know if it meets the Internet that you’ll be in the news. We need Secure Exposed Access! Sure, you could retool it. Add […]
-
Strong Identity and Authentication: Avoid Named User License Costs With Federation
Implement a srong, simple, secure authentication system, including support for 2-factor authentication, without triggering named-user license costs.
-

Two-Factor Herd Immunity: Mozilla 2-factor authentication
Mozilla makes multi-factor authentication mandatory for authors. Herd Immunity suggests if we get a few more, we are all protected.
-

Auth and API: OpenID Connect for user + service, and enforcement along route
Identity: Authentication a user in a simple, secure way, with two-factor authentication, and allowing the user to interact with API are the key to success.
-

Remove SMS from your 2-factor authentication
SMS (text) has no place in your 2-factor authentication world. Remove it now and rely on a physical device (e.g. YubiKey) or TOTP (e.g. Authenticator app).
-
What does your internal enterprise application login look like?
Whether your app is municipal, industrial, financial, or just vacation-booking-HR, it needs a strong, 2-factor auth system. Else you teach bad habits.
-

That’s the kind of password an idiot uses on luggage: cloud security
Passwords. bits of plain text that end up everywhere in automated systems. etcd. A `secure` way to share secrets. The Internet. A place that everything is guaranteed to end up. This is a toxic brew, read on!
-

Security of the upstream code, and, the importance of the egress firewall
Bad code can come in through our own import statements and software process. Do you run an egress firewall to protect the world from yourself?
-

Using single-sign-on oauth2 across many sites in Kubernetes
Learn how to safely protect ‘internal’ or ‘development’ resources while having them on the public Internet. Simply.