Auto-Create Users From Specific Domain With Google Workplace
Simplify Setup
The Agilicus Managed Upstream Providers option of ‘Google’ allows users to sign in with GMail and Google Workplace (G Suite) with zero-configuration. In some circumstances (for example, to enable the use of auto-create locked to a specific domain) you may wish to create your own Google Identity Provider setup.
Auto-Create Users From Specific Domain With Google Workplace
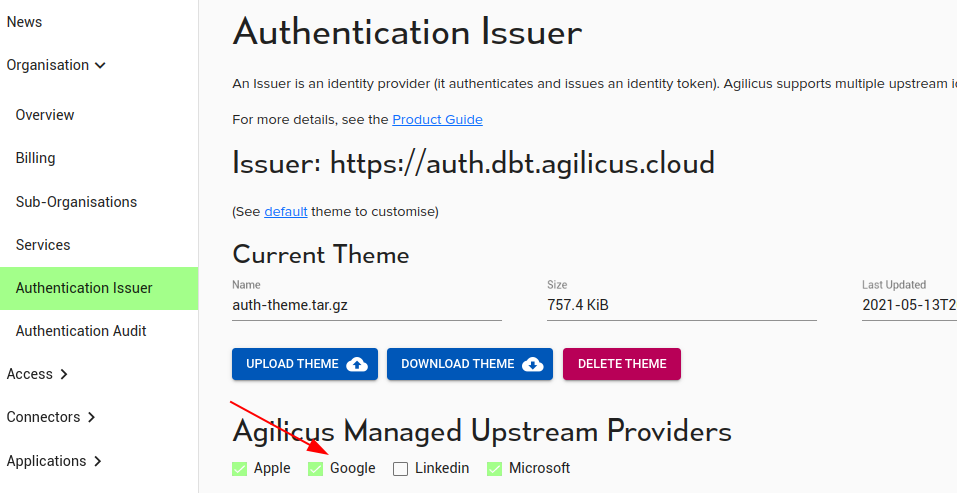
The Agilicus Managed Upstream Providers option of ‘Google’ allows users to sign in with GMail and Google Workplace (G Suite) with zero-configuration. In some circumstances (for example, to enable the use of auto-create locked to a specific domain) you may wish to create your own Google Identity Provider setup.
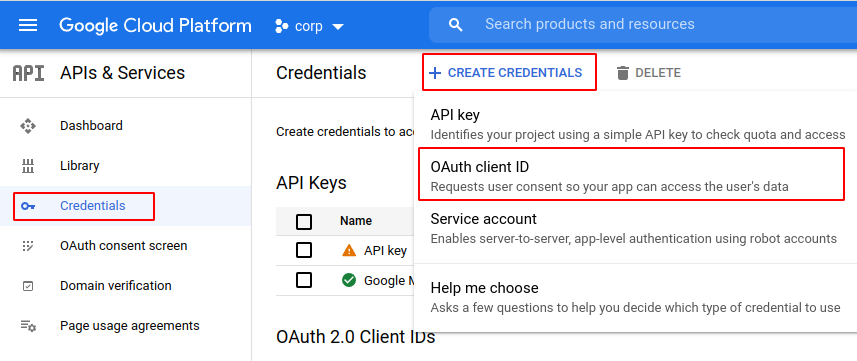
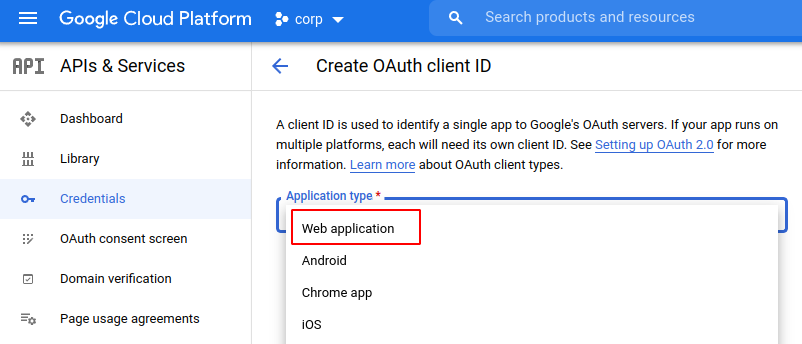
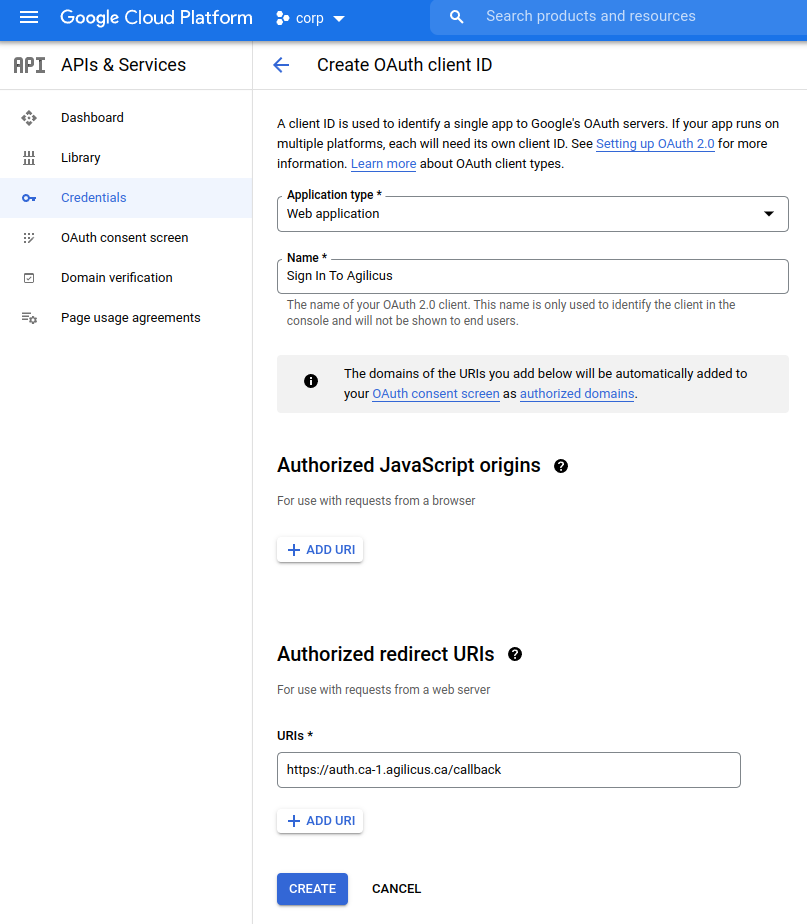
To do so, we will use the Google Console, create a Credential, OAUth2, Web application, and from there obtain a client-id and client-secret.
We will then configure the list of acceptable domains which may use it, and cross-configure this information into the Agilicus admin portal.
There is no general requirement to create your own Credentials in Google: do so if you wish finer-grained control by e.g. restricting source domain, or if you have specific audit requirements.
For more information see Google’s “Getting Started With Authentication“.
Navigate to https://console.cloud.google.com/apis/credentials . You may be prompted to enable the API for your organisation.
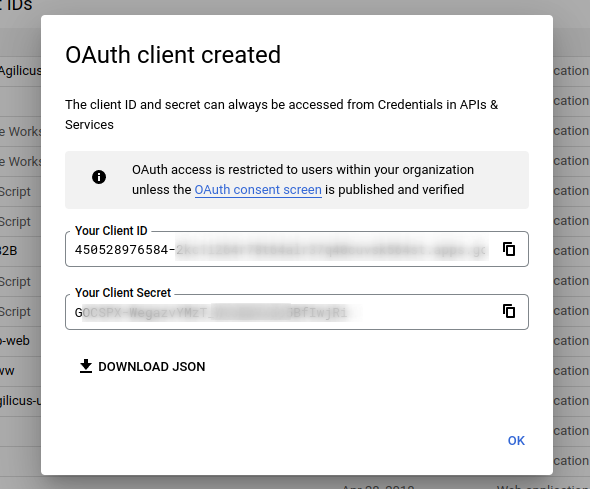
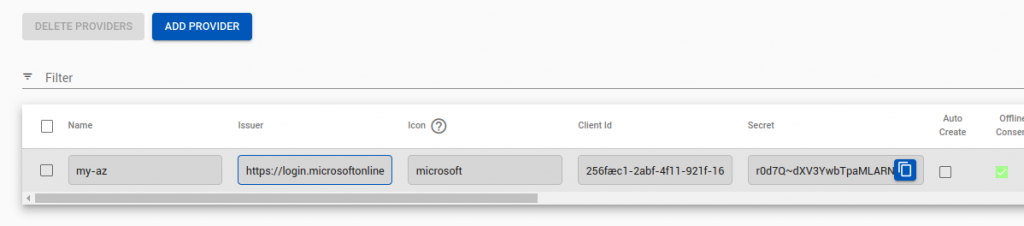
At this stage you will be given two facts (client ID, client secret). You will now enter these into the Agilicus Admin portal.
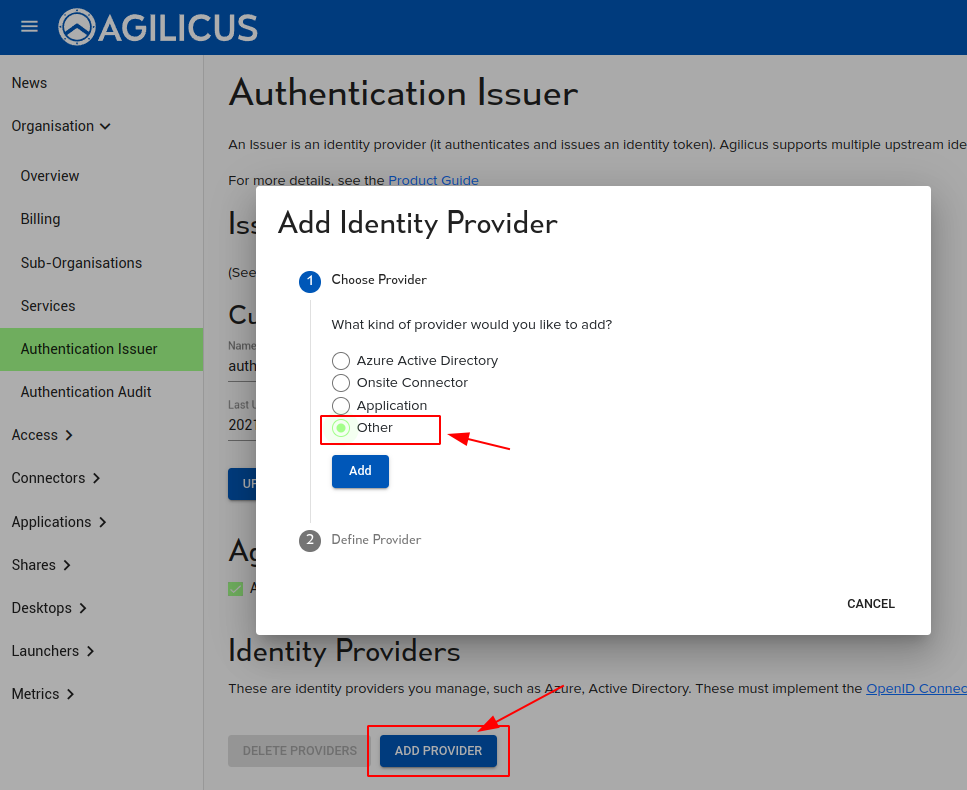
In the Agilicus Admin portal, add a new Identity Provider of type ‘Other’ (this is a generic OpenID Connect Identity Provider).
Enter a name (your users’ will see this, so e.g. “Agilicus Google Workplace”), the Issuer url (https://accounts.google.com), the Client ID (from above) and the Secret (from above).
You may wish to enable auto-create on this Identity Provider, in which case authenticated users will be automatically provisioned.
At this stage, you may wish to enable “Authorized Domains” in your Google Workplace settings.
Users may now sign in to the system via this Identity Provider.
Want Assistance?
The Agilicus team is here for you. The ‘Chat‘ icon in the lower left, here, or in the administrative web page, goes to our team.
Or, feel free to email support@agilicus.com
Not yet a customer? The TRY NOW button will walk you through the process.