You have probably used a product which used, or seen talk of, a CNAME. What is this? Why would you want it? How would you configure it? What does it do? When would you use it?
A CNAME is a “Canonical Name Record“. It is an entry in an Internet Name Server that maps one name onto another. In a nutshell, an alias. They were originally created to allow running multiple services on the same host (e.g. ‘www’ and ‘ftp’ and ‘smtp’). CNAME’s were standardised in RFC 1034 in 1987. Perhaps before you were born!
As an adminstrator, the most common use the CNAME has today is for services provided by a 3rd party that use your domain name. An example would be a Web Application Firewall. You might purchase such as service from a 3rd party, and, want them to handle the traffic to www.example.com. So, you would create a CNAME for www.example.com pointing to fw.waf.com, if they were called ‘waf.com’. This means that when one of your users opens their browser and types in ‘www.example.com’, they get back a record saying “if you really want to know where that is, we suggest looking up fw.waf.com”.
Why would you use a CNAME for this, rather than an A record (address, e.g. an IP address)? Well, ‘waf.com’ might have big plans. Someday they will move out of their parent’s basement and into a real cloud provider. They will have hundreds of servers in tens of countries. They don’t want to have to have all customers update DNS records for this growth. So, by giving you a pointer to something they control, waf.com can make their updates independent of you, the administrator of example.com.
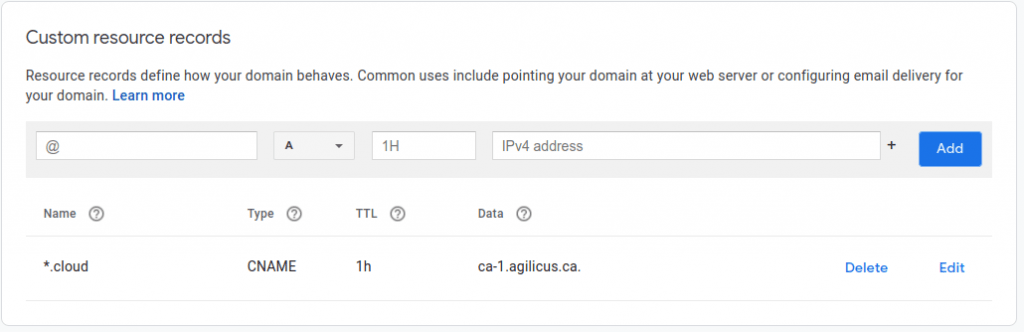
How do you configure a CNAME? Well, it will depend on your DNS provider. It is very likely they have a web-based interface, and it might vary. Below is how I would configure a CNAME for ‘*.cloud.example.com’ pointing to ‘ca-1.agilicus.ca’. Where did ‘example.com’ go in this screenshot you ask? Well, it is implicit, I am configuring the DNS for example.com, so the records omit that.
What does ‘*.cloud’ mean? Well, it means that foo.cloud.example.com, bar.cloud.example.com will both (and any name) resolve to ca-1.agilicus.ca.
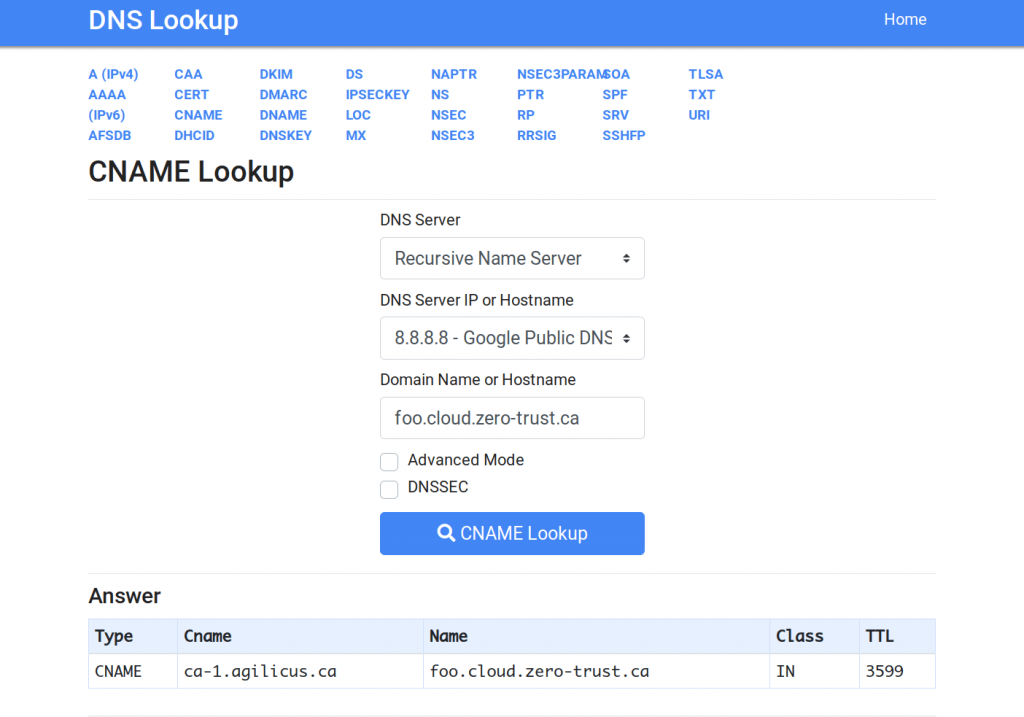
Now, how would you confirm you have created your CNAME properly? My favourite method is the command-line and a tool called ‘dig’.
$ dig -t cname foo.cloud.zero-trust.ca ; <<>> DiG 9.16.6-Ubuntu <<>> -t cname foo.cloud.zero-trust.ca ... ;; QUESTION SECTION: ;foo.cloud.zero-trust.ca. IN CNAME ;; ANSWER SECTION: foo.cloud.zero-trust.ca. 3600 IN CNAME ca-1.agilicus.ca.
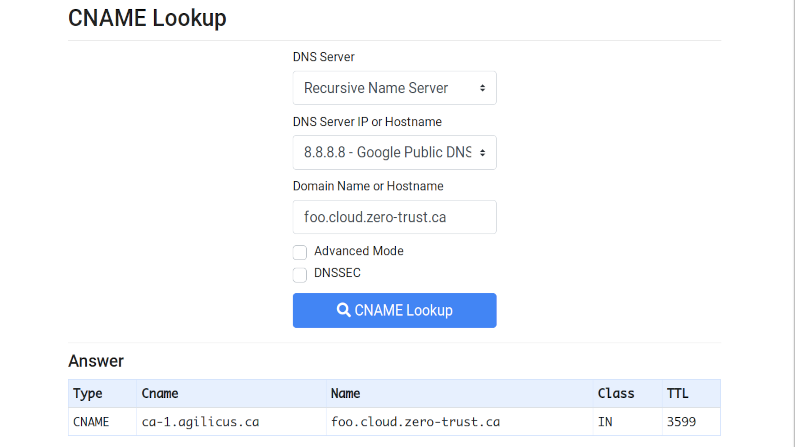
But, you can also use online web sites that will help you, e.g. https://dnslookup.online. You can see the result below. DNS takes time to propogate, so give it a few minutes. Also, the TTL (time to live) controls how long others will cache this. If in doubt, make this 5 minutes until you have your CNAME setup properly, and then use a longer time like 1 hour.