Zero Trust Security
Understand the fundamentals, key principles, standards, and best current practices.
What is Zero Trust?
The foundation of Zero Trust Security is switching from a perimeter-based (firewall and VPN) model of access to a user-to-resource model.
It means implementing strong, simple identity for both people and also a system. Decouple the identity from the corporation to make it affinitive to the user—a single identity.
Through it, you can enforce entitlements and authorization in the network.
This micro-segmentation is simpler to use, more accessible, and, more secure. It reduces the lateral traversal, empowers your users, increases your audit capabilities, is more economical, and is more scalable. This is the power of Zero Trust.
Zero Trust Security Standards
Identity
The core of any Zero Trust Architecture is identity. Identity of a person, identity of a resource. Users are commonly identified via OpenID Connect and SAML. Resources are commonly identified by Client Certificates.
Zero Trust Architecture
Zero Trust Architecture has evolved over the years. The constant theme is changing from a perimeter-based (firewall+VPN) security stance to a user+resource stance.
Foundational
Zero Trust Security has a set of foundational standards that are shared with other technologies. These relate to cryptography, security, and identity.
Best Practices
-

Begone Ivanti Industrial VPN Sayeth CISA
Read more: Begone Ivanti Industrial VPN Sayeth CISAED 24-01 directs agencies to instantly remove Ivanti Industrial VPN from industrial operations. Defence In Depth, Zero Trust give you more time to react.
-

Using Zero Trust to Enable Secure Remote Access to SCADA for Water Systems
Read more: Using Zero Trust to Enable Secure Remote Access to SCADA for Water SystemsThis blog post explores the challenges of securing remote access to SCADA systems and how Zero Trust can act as a solution.
-

Zero Trust vs. VPN: A Comprehensive Comparison for Secure Remote Access
Read more: Zero Trust vs. VPN: A Comprehensive Comparison for Secure Remote AccessIn this blog post, we’ll dive into the Zero Trust vs. VPN security model differences and why the former is ultimately the far superior choice for secure, seamless remote access.
-

SSH for Remote Access: Every User, Every Device, Every Application
Read more: SSH for Remote Access: Every User, Every Device, Every ApplicationIn this blog post, we’ll delve into the challenges of enabling SSH for remote access and how you can do so without compromising security through Zero Trust.
-
Simplifying Secure Access: Enabling Rockwell Automation Remote PLC Access Without a VPN
Read more: Simplifying Secure Access: Enabling Rockwell Automation Remote PLC Access Without a VPNIn this post, we’ll explore the limitations of VPNs and delve into how to enable VPN-less Rockwell Automation remote PLC access.
-
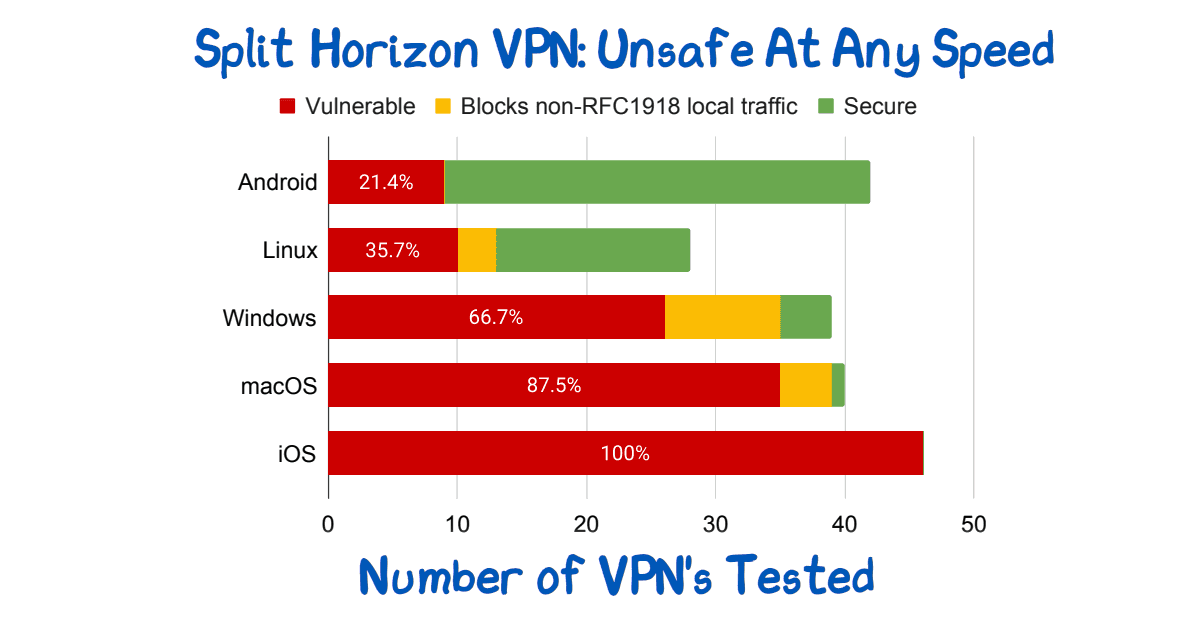
Split Horizon VPN: Unsafe At Any Speed
Read more: Split Horizon VPN: Unsafe At Any SpeedSplit Horizon VPN’s are used to avoid breaking video conferencing. They are unsafe. See paper for route injection issues.
-

NIST sp 800-63A: Introduce Yourself
Read more: NIST sp 800-63A: Introduce YourselfWho are you? Identity involves knowing who you are, and then later proving it. NIST sp 800-63A enrollment is the first step, let’s talk about that!
-

The Security Risks of Using VPNs in Water and Wastewater Facilities
Read more: The Security Risks of Using VPNs in Water and Wastewater FacilitiesWhat are the risks of using VPNs in water and wastewater facilities? We’ll help you answer that question and understand what to do instead.
-

The Security Risks of Using Shared Credentials in Water and Wastewater Facilities
Read more: The Security Risks of Using Shared Credentials in Water and Wastewater FacilitiesThere are many security risks of using shared credentials in water and wastewater facilities. Here’s why you should eliminate them and how to do it.
-
Zero Trust Troika: The Who, The What, The How
Read more: Zero Trust Troika: The Who, The What, The HowPerimeter security approaches are no longer effective. A Zero Trust Network Architecture is a powerful, modern way to protect your network from cyber attacks.
-

Strengthen Your Industrial Network Cybersecurity with Vendor Access Management
Read more: Strengthen Your Industrial Network Cybersecurity with Vendor Access ManagementSecuring your third-party vendors can help reduce the cyber risk to your control systems and improve overall industrial network cybersecurity.
-

Understanding the CISA Zero Trust Maturity Model: A Framework to Improve Your Security Posture
Read more: Understanding the CISA Zero Trust Maturity Model: A Framework to Improve Your Security PostureThis article will give you an overview of the CISA Zero Trust Maturity Model, the changes made in Version 2.0, and how it can benefit your organization.
-

The Zero Trust Roadmap: Understanding NIST 800-207 and How to Align With It
Read more: The Zero Trust Roadmap: Understanding NIST 800-207 and How to Align With ItThis article will give you an overview of NIST 800-207 and the different ways your organization can implement Zero Trust to meet the guidelines.
-
Best Practices In Vendor Privileged Access Management
Read more: Best Practices In Vendor Privileged Access ManagementVendor privileged access management best practices: Access control, strong, unified authentication, fine-audit, secure access.
-

Identity Provider Versus Single-Sign-On
Read more: Identity Provider Versus Single-Sign-OnSingle-Sign-On and Identity Providers are often treated as the same. But, the IdP facilitates the SSO. You can have multiple IdP if desired.
-

Who Are You? Prove It! Identity Versus Authentication
Read more: Who Are You? Prove It! Identity Versus AuthenticationIdentity vs Authentication. Who are you. Prove it. Related but different concepts. Ensure your IdP does not give identity when it realy means authentication.
-
Another Day, Another Exploit – Protecting Against the ProxyNotShell Exchange Server Zero-Day Vulnerability
Read more: Another Day, Another Exploit – Protecting Against the ProxyNotShell Exchange Server Zero-Day VulnerabilityLearn how zero trust protects against the new Microsoft Exchange Server zero-day exploit affecting Outlook Web Access (OWA), ProxyNotShell. With Agilicus, you’ll block lateral traversal and prevent unauthorised traffic from arriving at your resources while ensuring they are still accessible to legitimate users.
-

Well Timed or Coincidental, Cue the Phishing Attacks as 2.5M Students Affected by Data Breach
Read more: Well Timed or Coincidental, Cue the Phishing Attacks as 2.5M Students Affected by Data BreachDays after announcing student loan forgiveness in the United States, 2.5 million student borrowers had their personal information exposed in a data breach and are at an increased risk of being targeted in a phishing attack.
-

Protecting Against the OWASP Top 10 Web Application Vulnerabilities
Read more: Protecting Against the OWASP Top 10 Web Application VulnerabilitiesThe OWASP Top 10 is a standard awareness document that outlines the most critical web application security risks and vulnerabilities. Learn how Agilicus AnyX is designed to eliminate an attacker’s visibility into the potential OWASP Top 10 web application vulnerabilities.
-

Industrial Air Gap – A Tale Of 2 Users
Read more: Industrial Air Gap – A Tale Of 2 UsersIndustrial devices are hard to secure. Commonly done only via direct local access. Teams, however, wish remote access to improve efficiency. A solution to this battle is Zero Trust.
-

Top 5 Cybersecurity Resolutions to Cross off Your List in 2022
Read more: Top 5 Cybersecurity Resolutions to Cross off Your List in 2022Cybercriminals had a record year, the cost of a breach reached new highs in 2021. With clear cybersecurity goals, businesses avoid becoming a news headline.
-

NIST sp 800-63A: Introduce Yourself
Read more: NIST sp 800-63A: Introduce YourselfWho are you? Identity involves knowing who you are, and then later proving it. NIST sp 800-63A enrollment is the first step, let’s talk about that!
-
NIST sp 800-63B: How Well Do I Know You?
Read more: NIST sp 800-63B: How Well Do I Know You?Zero-Trust Network Architecture has 3 steps: Authenticate (Who), Authorise(What), Access(How). 3 Levels of strength of the who are defined in NIST sp 800-63B. Does the goldilocks principle apply to you? Read on!
-
Zero-Trust Remote Access to Fix VoIP DDoS
Read more: Zero-Trust Remote Access to Fix VoIP DDoSReconfigure a VoIP PSTN gateway remotely via Zero Trust with Multi-Factor Authentication and single-sign-on to avoid a DDoS.
-

Authentication, Authorisation, and API Keys
Read more: Authentication, Authorisation, and API Keyse encouraged to create API keys by many SaaS tools, and, these present real authorisation challenges.
-
Mind the gap between the web app and the desktop
Read more: Mind the gap between the web app and the desktopWe want a web app. We have a desktop. Use zero-trust to make any desktop available to any device without a VPN.
-

A ’round tuit’ to get your internal web apps available
Read more: A ’round tuit’ to get your internal web apps availableYou have an internal tool. Grafana, Prometheus, …. You get an alert, its via Slack, Chat, etc. You click. The link goes nowhere. You curse. We fix!
-
The Pipeline Ransomware Came Via The VPN
Read more: The Pipeline Ransomware Came Via The VPNA criminal group takes over a nations energy via a VPN. Its time to treat the VPN as a risk, not a security solution. Zero Trust is better.
-
SSH To Server. No IP? No Problem!
Read more: SSH To Server. No IP? No Problem!SSH to the server fleet. No Public IP? No problem. No VPN. No firewall changes. End-to-end encryption. Any user.
-

Keep The Share, Ditch The Ransomware With Zero Trust
Read more: Keep The Share, Ditch The Ransomware With Zero TrustKeep The Share. Ditch The Ransomware. Simple Zero-Trust allows any user, any device, any share, no VPN, no ransomware. Simple single sign-on.